
For startups, the incorporation of the accounting equation into their financial practices is crucial for viability and sustainability. In the the accounting equation is usually expressed as early stages, entrepreneurs often utilize this equation to examine their financial positions closely. For instance, when a startup invests in inventory (an asset), they may use a loan (liability) to finance this acquisition. As expected, the sum of liabilities and equity is equal to $9350, matching the total value of assets.
What about drawings, income and expenses?

Creditors include people or entities the business owes money to, such as employees, government agencies, banks, and more. $10,000 of cash (asset) will be received from the bank but the business must also record an equal amount representing the fact that the loan (liability) will eventually need to be repaid. Required Explain how each of the above transactions impact the accounting equation and illustrate the cumulative effect that they have.
Impact of transactions on accounting equation
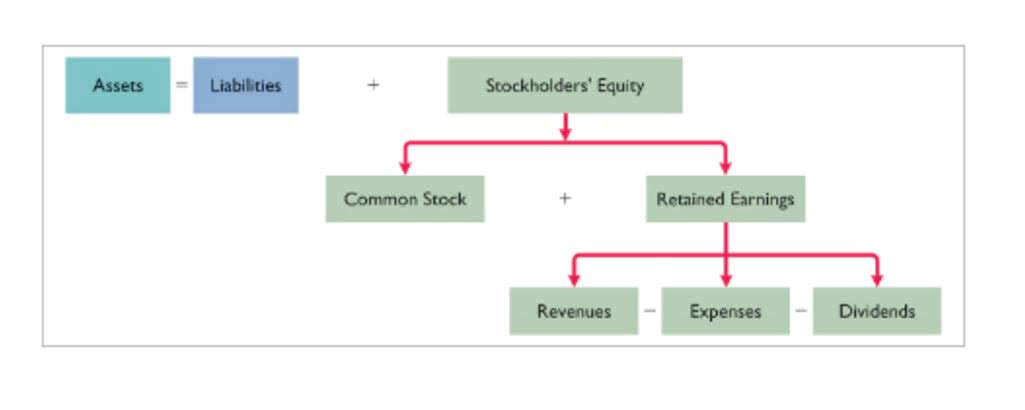
Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities. It can be found on a contra asset account balance sheet and is one of the most important metrics for analysts to assess the financial health of a company. This straightforward relationship between assets, liabilities, and equity is the foundation of the double-entry accounting system. The accounting equation ensures that the balance sheet remains balanced.
- That part of the accounting system which contains the balance sheet and income statement accounts used for recording transactions.
- Want to learn more about recording transactions and doing accounting for your small business?
- Most sole proprietors aren’t going to know the knowledge or understanding of how to break down the equity sections (OC, OD, R, and E) like this unless they have a finance background.
- Double-entry bookkeeping is a system that records transactions and their effects into journal entries, by debiting one account and crediting another.
- If it doesn’t, then your books are out of balance, most likely because there was an entry made to an owner’s equity account that isn’t reflected in your calculation above.
- The accounting equation’s left side represents everything a business has (assets), and the right side shows what a business owes to creditors and owners (liabilities and equity).
- After six months, Speakers, Inc. is growing rapidly and needs to find a new place of business.
Let’s get more productive
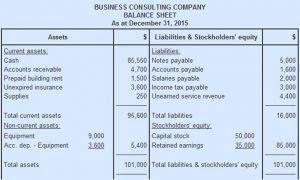
The balance sheet is a more detailed reflection of the accounting equation. It records the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity of a business at a specific time. Just like the accounting equation, it shows us that total assets equal total liabilities and owner’s equity. One of the main financial statements (along with the balance sheet, the statement of cash flows, and the statement of stockholders’ equity). The income statement is also referred to as the profit and loss statement, P&L, statement of income, and the statement of operations. The income statement reports the revenues, gains, expenses, losses, net income and other totals for the period of time shown in the heading of the statement.
- Thus, equity is not only a critical component of the accounting equation but also an essential indicator of a company’s financial health and operational effectiveness.
- It’s essentially the same equation because net worth and owner’s equity are synonymous with each other.
- By applying the principles of the accounting equation to real-world scenarios, stakeholders can enhance their strategic decision-making capabilities, thereby fostering financial growth and stability.
- For example, publicly traded companies regularly report their financial status, showcasing how their assets and liabilities align with shareholders’ equity.
How Does the Accounting Equation Differ from the Working Capital Formula?
- The accounting equation doesn’t consider these currency transactions, which gives a false view of a company’s financial position if it is operating globally.
- By comparing its assets, liabilities, and equity, you can quickly assess whether a company has enough resources to cover its debts.
- Unearned revenue from the money you have yet to receive for services or products that you have not yet delivered is considered a liability.
- The income statement will explain part of the change in the owner’s or stockholders’ equity during the time interval between two balance sheets.
- It specifically highlights the amount of ownership that the business owner(s) has.
- The accounting equation, which states that assets equal liabilities plus equity, serves as the foundation for analyzing a company’s financial health.
The accounting equation plays a significant role as the foundation of the double-entry bookkeeping system. It is used to transfer totals from books of prime entry into the nominal ledger. Every transaction is recorded twice so that the debit is balanced by a credit. The accounting equation helps in financial analysis by evaluating a company’s current financial health. By comparing its assets, liabilities, and equity, you can quickly assess whether a company has enough resources to cover its debts. For example, if a law firm chart of accounts company’s assets are more than its liabilities, it’s a good sign indicating a strong financial position.
From the Statement of Stockholders’ Equity, Alphabet’s share repurchases can be seen. Their share repurchases impact both the capital and retained earnings balances. Equity is named Owner’s Equity, Shareholders’ Equity, or Stockholders’ Equity on the balance sheet. Business owners with a sole proprietorship and small businesses that aren’t corporations use Owner’s Equity. Corporations with shareholders may call Equity either Shareholders’ Equity or Stockholders’ Equity. Incorrect classification of an expense does not affect the accounting equation.